Blog

This nodal adds parametric controls of high and low lights, and additional adjustment of luminous and chromatic contrast in S-shaped, usual way to achieve a "pleasant tone".
To use a Color Surface it is recommended to use only the Gamma control of any of the nodes.
To make the functionality compatible with the free version of DaVinci Resolve, the invert is performend by a 1D-LUT and not with a DCTL.
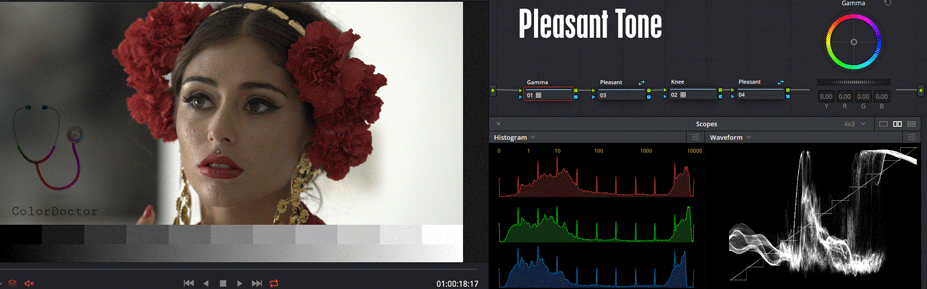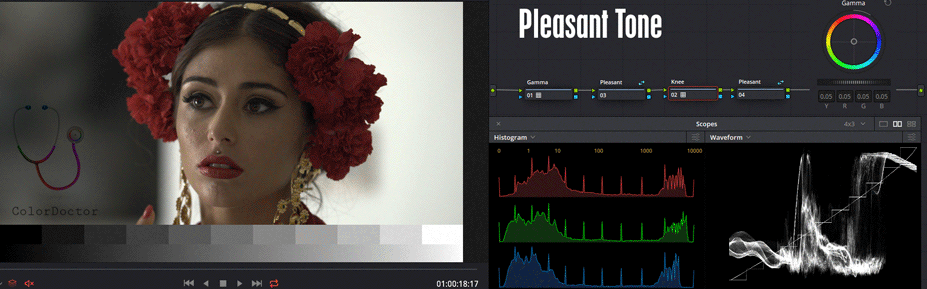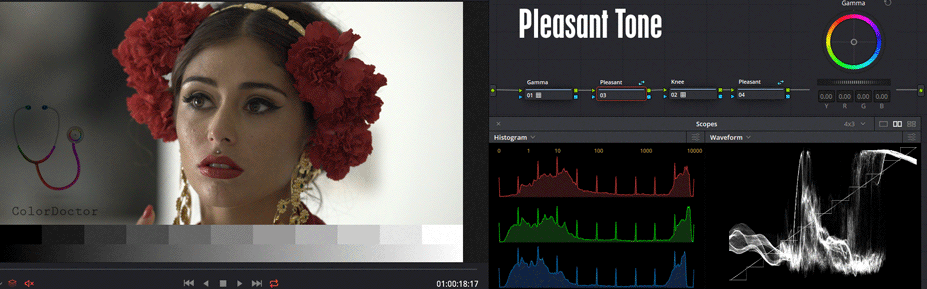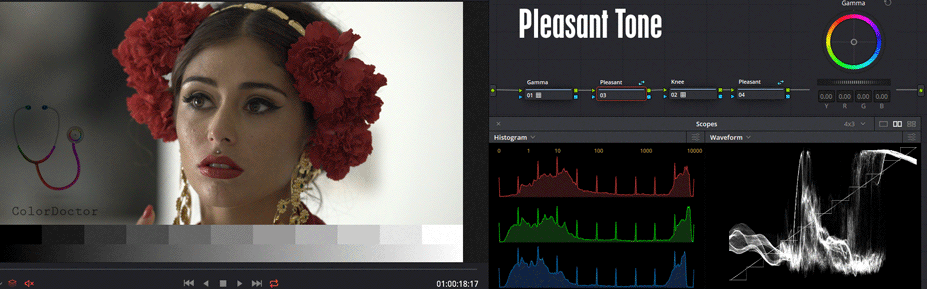
Gamma
This first node works regularly. It is recommended to reserve it to edit the Gamma parameter, aimed to work both the brightness and the color of the low lights.
In its output it has a 1D-LUT Output-> Invert which will enable the particular behavior of the following nodes.
Knee
This third node is recommended to reserve it to edit only the Gamma parameter, aimed to work both the brightness and the color of the highlights, working as a parametric control of the contrast curve in the high zone, also understood as a "Knee" control.
This node receives the inverted action of the previous nodes, but returns to invest in its output with an additional 1D-LUT Output-> Invert that returns the action to its natural state.
Pleasant
This node appears twice in the nodal because it is a Shared Node which repeats before and after the Knee node.
From either of the two copies of this node, you can edit Gamma from the slider or ring, to adjust the contrast pleasingly. From the ball, you can define a color to tint the highs and lows with complementary colors.
Due to the inversions, the balls of the first and fourth node work aligned to the Vectorscope, while the second and third node will work with inverted balls.
Link to the .drx here.
This node adds more "saturation" controls.
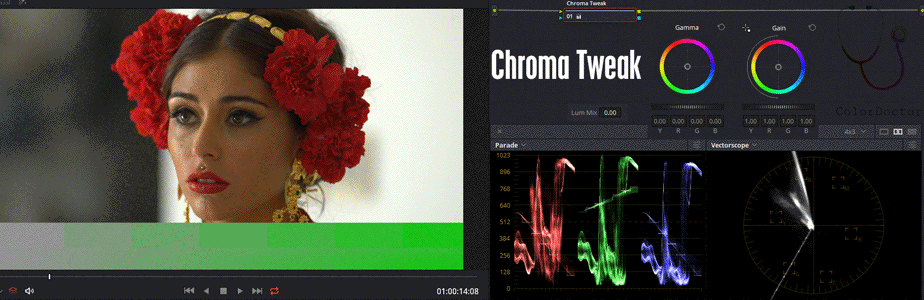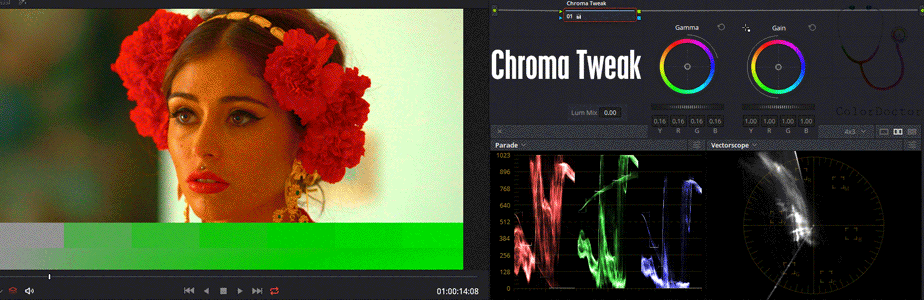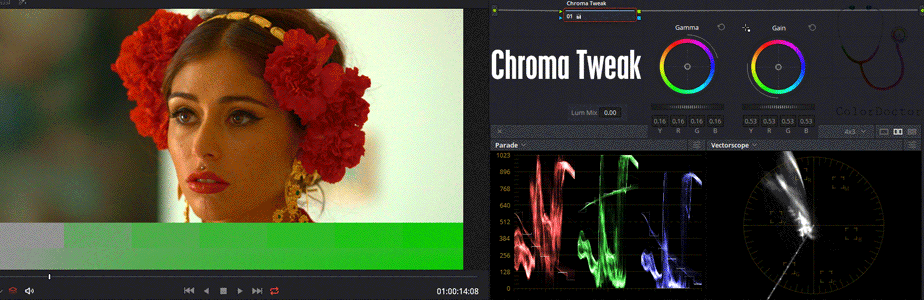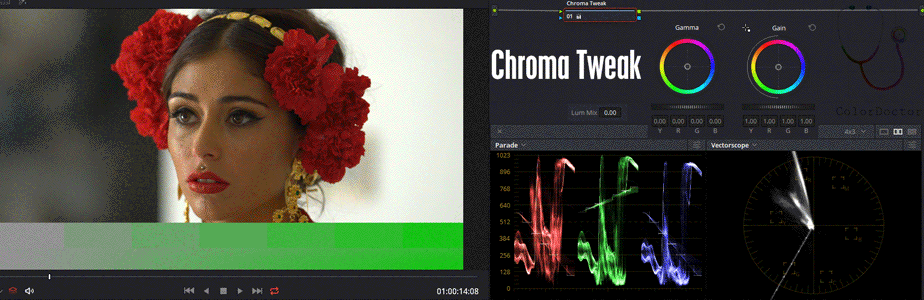
This node works in the Y'UV "colorspace" an inaccurate terminology which actually defines that the node works under another color encoding, or what is also understood as a color model.
When changing a work mode node, the color space does not really change (if you work in Rec.709, this node will not modify the working gamut for example).
It has inhibited the influence on the Y channel (Channel 1), thus restricting its action on chromaticity, expressed by the UV components.
For correct operation, the Lum Mix parameter must be set to zero.
The user can modify Gain as ordinary saturation control but also can edit Gamma to alter the values of low saturation with greater influence.
To keep the most saturated values unchanged, it is necessary to increase Gamma and lower Gain in the proper proportion.
This node can then be controlled by a Color Surface.
Link to the node here.
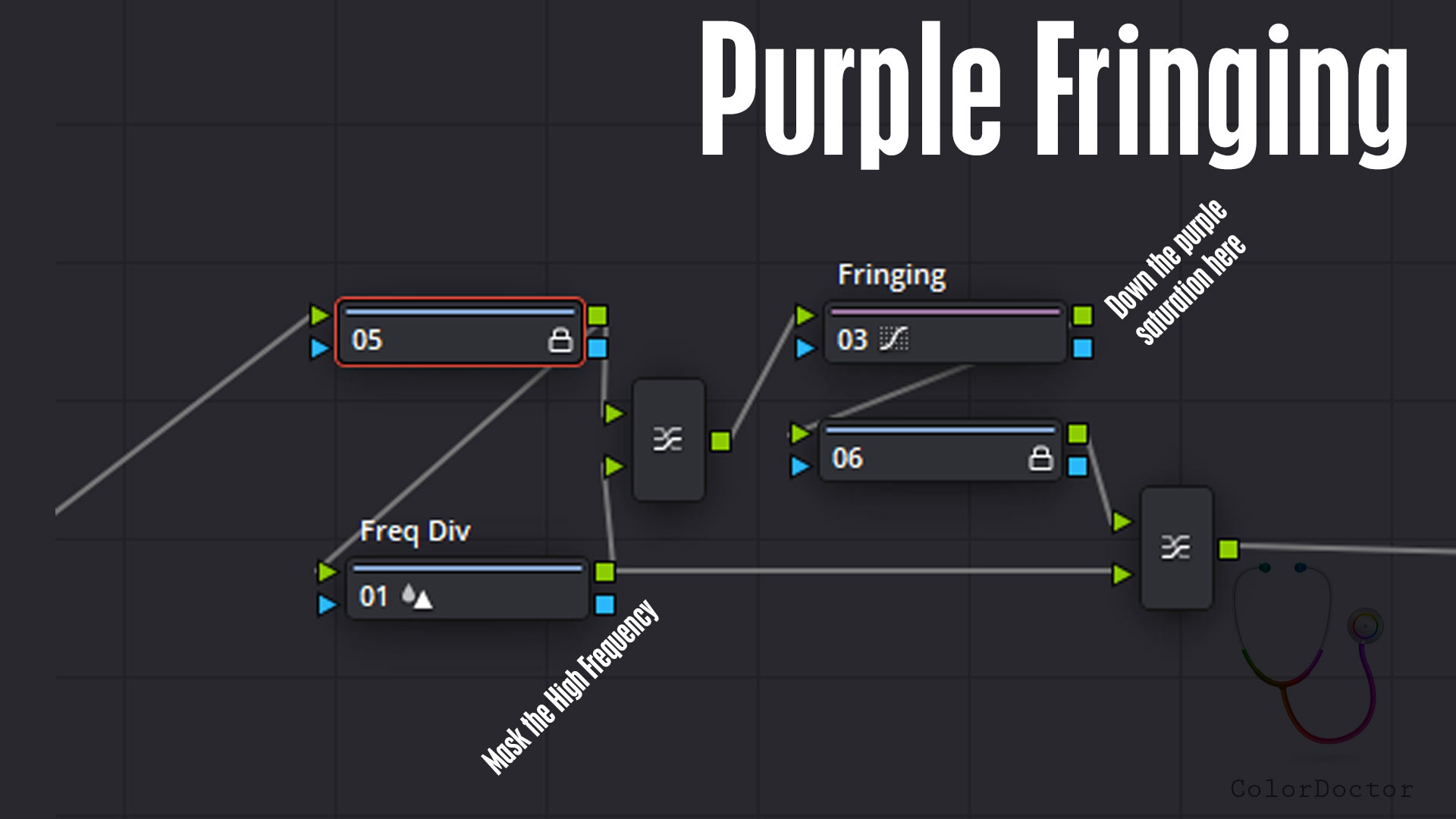
This nodal is useful for removing chromatic aberrations at high frequencies. This optical problem is usual to find around overexposure zones, where white seems to be surrounded by a purple border.
This border can also be seen in other colors, and the nodal will serve for any of the colors caused by the aberration, adding more points in the curve Hue vs. Sat.
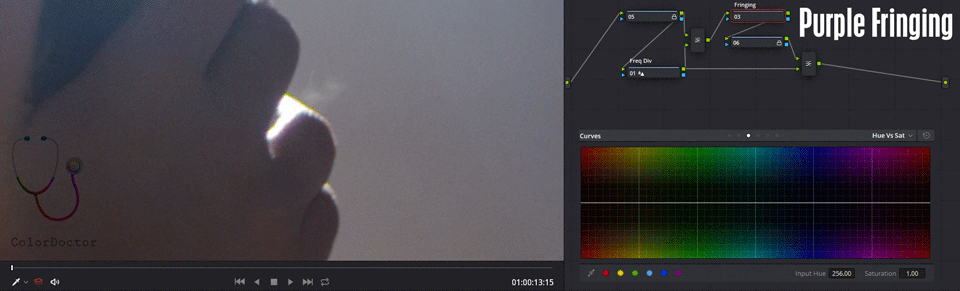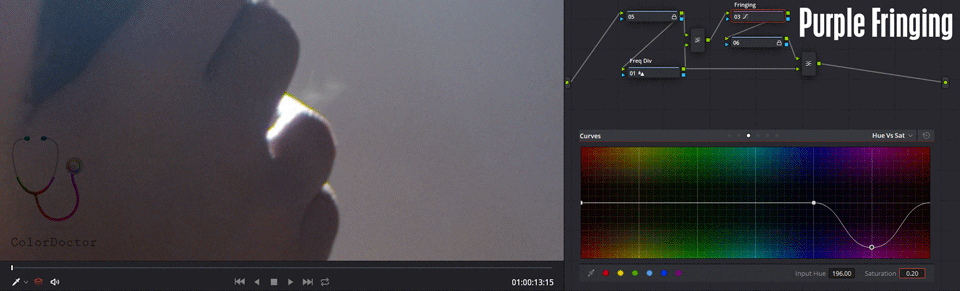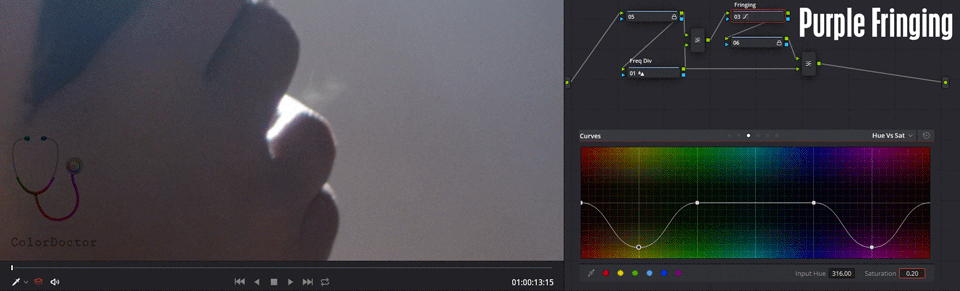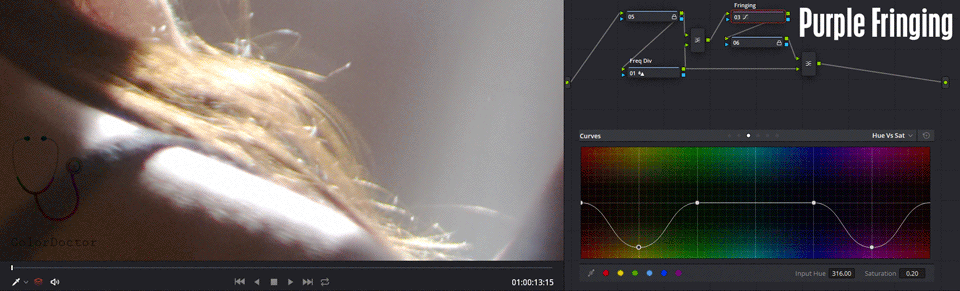
Freq Div
This node has the parameter Blur> Radius edited, with which the spatial frequency that the chromatic aberration has is divided. The higher the value, the smaller the edge size where the next node will operate.
Fringing
This node has the Hue vs. Sat curve edited and with the magenta color with Sat 0.2 in such a way that by default it desaturates the characteristic color resulting from the chromatic aberration.
In some cases, the border color can also be yellow, and to attenuate it, add a point of yellow in the same curve and decrease saturation.
The blocked nodes keeps only the bypassing. Thanks to that the user can disable the Fringing node and the node tree does not lose its neutral action.
Link to .drx here.
